Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where traditional systems often fail, innovation becomes a necessity. From the rise of the Internet to the evolution of digital currencies, people have been constantly searching for more secure, transparent, and efficient solutions. One such groundbreaking technology that has revolutionized back in 2009 is blockchain, the underlying foundation of cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, a digital currency that has become the best combo in the ledger world. Blockchain technology provides a decentralized, secure, and transparent solution, minimizing these challenges.
Let’s make it easier with the different scenarios.
Ajay, a real estate investor, is interested in purchasing a vacation property from Abhishek. Both parties agree on the terms, including the sale price and payment structure. However, once the transaction begins, differences arise. Ajay believes Abhishek has received the payment, but Abhishek denies having received the full amount, and now creating a conflict.
With proper ledger and contracts, these fraudulent activities can be minimized and made into immutable records with high transparency.
Let’s explore the intriguing world of ledgers and discover the exciting aspects of blockchain technology together! SWA MLM Software has prepared an article about blockchain technology. Let’s Make it easier for you to understand how blockchain technology works.
Now you must be wondering what blockchain technology is.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system primarily designed to validate and securely process transactions. But what does validation mean in this context? A ledger system records all transactions within the network, and the blockchain approach ensures that every transaction is found meaningful is legitimate by preventing any misrepresentation.
Key Terms in Blockchain Technology
- Digital Wallet
A software application that enables users to send, receive, and securely store cryptocurrency. It acts as a digital bank for blockchain transactions. - Ledger
A digital record that logs all transactions within the blockchain network. The ledger is open to participants, ensuring transparency and trust. - Nodes
Interconnected computers distributed worldwide validate and verify every transaction in the blockchain network, ensuring accuracy and security. - Public Key
A cryptographic code generated from the private key is used to receive cryptocurrency. It acts as an address that others can use to send funds. - Private Key
A unique cryptographic key that allows users to access and control their cryptocurrency, enabling them to send funds. Only the wallet owner has access to this key, ensuring security.
How Blockchain Technology Transaction Works?
When Ajay initiates a transaction, several steps are taken to ensure the process is secure and valid:
- Balance Check:
Ajay’s wallet first verifies whether he holds the required amount of Bitcoin (in this case, 2 BTC). The wallet uses its private key to confirm the available funds. - Node Validation:
After the balance is verified, a network of nodes becomes involved. Nodes are distributed computers located around the world that assist in validating transactions. Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain and utilizes advanced computing power to ensure the accuracy of the data. These nodes collaborate to validate transactions and secure the network. - Transaction Validation:
Verification of Ownership: Nodes ensure that the source of the transaction is Ajay’s wallet. This prevents unauthorized access or transactions.
History Tracking: To ensure that Ajay has enough Bitcoin, all previous transaction inputs are reviewed. These inputs act as references to verify the legitimacy of the current transaction. - Approval and Confirmation:
After validating the details, nodes approve the transaction. Once approved, Ajay’s wallet is debited with 2 BTC, and Abhishek’s wallet is credited with the same amount—2 BTC. - Confirmation: Finally, nodes confirm the transaction once again, ensuring that Ajay’s wallet reflects a decrease of 2 BTC and Anna’s wallet demonstrates an increase of 2 BTC
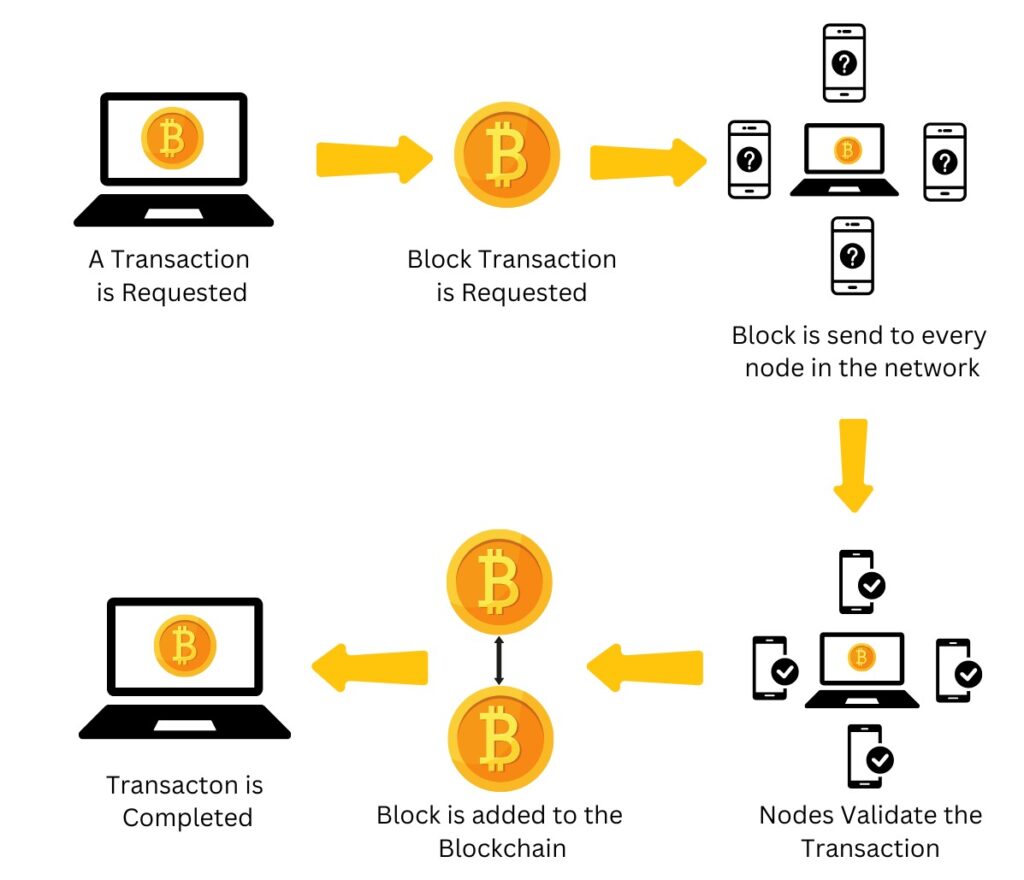
How Blockchain Technology Transaction Works
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Decentralization: Blockchain’s decentralized structure removes the need for intermediaries, cutting costs while enhancing transparency in transactions.
Security: Transactions are protected by cryptographic techniques to ensure that the integrity of the ledger is maintained, safeguarding sensitive information from hacks or fraud.
Transparency: All participants in a blockchain transaction have access to a shared, unalterable record, promoting openness and minimizing the risk of disputes.
Efficiency: Blockchain processes transactions swiftly and efficiently, significantly reducing the time and expenses associated with traditional methods.
Trust: The secure and transparent nature of blockchain fosters greater trust between parties, strengthening relationships and collaboration in transactions.
Cost Effective: As the blockchain does not need a third person it reduces the cost of the businesses and trust to other businesses.
Differences Between Blockchain Technology and Traditional Financial Systems
Now that we’ve covered how a Bitcoin transaction works, let’s highlight the key differences between blockchain technology and traditional financial institutions:
- Decentralization vs. Centralization:
In a traditional financial institution, transactions are controlled by a centralized entity like a bank. These transactions are private, with a centralized team responsible for processing and maintaining records.Meanwhile, blockchain operates on a decentralized network where data is open to the public. This means that anyone can access the transaction history, and no central authority governs the process. However, one cannot alter this data without the approval of a connected network.

- Transparency
With blockchain, every transaction is recorded on a distributed ledger visible to all participants. There’s no need for intermediaries to validate transactions, and everyone on the network has access to the data.
Meanwhile, in traditional systems, only authorized personnel handle transactions, and information is often kept confidential. - Security and Immutability
Blockchain employs cryptographic algorithms to secure data, making it immutable. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered.On the other hand, in a centralized system, transactions can be subject to manipulation or errors, depending on the reliability of the bank’s database.
- Responsibility and Risk:
In blockchain, users must take responsibility for their transactions, as there’s no customer support team to assist with errors or disputes.
This open-source nature allows for a higher level of security but also places the onus on users to understand the technical aspects.
Blockchain technology addresses the limitations of traditional systems by offering a transparent, secure, and decentralized solution. A simple representation of its functionality shows how transactions are grouped into blocks, validated, and then added to the blockchain. This process ensures integrity and trust from the initial transaction to its completion in the network.
How Does Blockchain Work? Understanding the Technical Side
Now that you understand the basics of blockchain, let’s delve into the technical workings of this revolutionary technology. At the core of blockchain’s functionality lie two essential components: private keys and public keys.
Private and Public Keys: The Cornerstones of Blockchain Transactions
When a blockchain transaction is initiated, a unique pair of keys—private key and public key—is automatically generated. These keys ensure the security, authenticity, and integrity of transactions.
What Are Private and Public Keys?
- Private Key:
- A private key is a confidential, cryptographic identifier known only to the owner of the wallet.
- It is used to sign transactions, granting the owner the authority to manage and transfer their digital assets.
- Because it is never shared, the private key ensures that only the rightful owner can initiate transactions.
- Public Key:
- A public key is generated alongside the private key and is shared openly within the blockchain network.
- It is used to validate transactions and verify the identity of the sender, without exposing the private key.
How They Work Together:
When a transaction, such as Ajay sending 2 BTC, is initiated:
- The private key is used to generate a digital signature, a unique cryptographic string tied to the specific transaction.
- The public key decrypts the digital signature during the validation process to confirm the transaction’s authenticity and ensure it originated from Ajay.
The Process of Blockchain Verification
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how blockchain works during a transaction:
- Transaction Initialization:
Ajay decides to send 2 BTC to Abhishek. Her private key generates a digital signature for this transaction, ensuring its authenticity and linking it exclusively to her wallet. - Broadcasting the Transaction:
The transaction, along with the digital signature, is broadcast to the entire blockchain network, which consists of distributed nodes. - Validation by Nodes:
Each node independently validates the transaction by:- Verifying the digital signature using Ajay’s public key.
- Ensuring Ajay has sufficient funds in her wallet.
- Confirming the transaction follows blockchain protocols.
- Consensus Mechanism:
- Nodes within the blockchain network use consensus algorithms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to agree on the validity of the transaction.
- This decentralized agreement ensures no single entity has control over the transaction process.
- Adding the Transaction to the Blockchain:
Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block, which is then linked to the previous block, forming an immutable chain of data. - Ledger Update:
- The blockchain ledger is updated to reflect the transaction. 2 BTC is debited from Ajay’s wallet, and Abhishek’s wallet is credited with the same amount.
- This update is visible to all participants in the network, ensuring transparency.
The Role of Digital Signatures
Digital signatures play an important role in blockchain transactions:
- They provide proof of ownership and authorization.
- Each transaction has a unique digital signature, making it impossible to duplicate or alter.
- Combined with public keys, they ensure that only the rightful owner can authorize a transaction.
Public and Private Key Access
- Public Key:
- Accessible by anyone in the network.
- Used to validate transactions securely.
- Private Key:
- Known only to the owner of the wallet.
- Grants full control over digital assets.
Storing and Validating Transactions
Every transaction is stored in the blockchain ledger after successful validation. The decentralized nature of the blockchain network ensures that no single entity controls or alters transaction data. The distributed nodes collectively validate and store each transaction, providing transparency and security.
Advanced your business goals with Cryptocurrency MLM Software
Solving the Puzzle Behind Blockchain Transactions
Mining is an important process in blockchain technology, allowing transactions to be validated and recorded. In the world of Bitcoin, mining is how new coins are created and added to the blockchain.
Let’s dive into how this process works and why it’s essential.
What is Mining?
When a blockchain transaction is initiated, it undergoes a validation process before being confirmed. Until validated, the transaction remains in an “unconfirmed transaction pool.” The validation happens through mining, where miners solve complex mathematical problems to confirm transactions and add them to the blockchain.
The Mining Process: Step by Step
- Mathematical Problem Generation:
Each transaction generates a unique problem using a cryptographic hashing algorithm. Solving this problem isn’t straightforward. Nodes on the network select transactions from the unconfirmed pool, attempt to validate them and solve the problem. - Hash Generation and Nonce Adjustment:
A 256-bit hash, represented in hexadecimal form (using 0-9 and A-F), is created. To solve the problem, miners adjust a 32-bit field value called a “nonce” to match specific conditions.
For example, the goal might be to produce a hash with trailing 15 bits as zeros. This requires significant computational effort and time.
Example of a hash:
8F434346648F6B96DF89DDA901C5176B10A6D83961DD3C1AC88B59B2DC327AA4
Solve the last 15 bits (88B59B2DC327AA4) to create:
8F434346648F6B96DF89DDA901C5176B10A6D83961DD3C1AC000000000000000. - Validation and Reward:
Once the problem is solved, the solution is shared across the network. Other nodes verify the solution, and if correct, the transaction is validated, and a new block is added to the blockchain. The miner who solves the problem is rewarded, typically in Bitcoin.
Technology Behind Mining
The mining process operates using a “Proof of Work” (PoW) mechanism, relying on the SHA-256 cryptographic algorithm. This ensures security and efficiency in generating hashes for each transaction.
Each block in the blockchain includes the current transaction data and a reference to the previous block, creating a continuous, secure chain of records.
Mining Rewards and Challenges
Initially, miners receive significant rewards (e.g., 12.5 BTC) for solving blocks. However, as mining progresses:
- Difficulty Increases: The computational effort required becomes more challenging over time.
- Rewards Decrease: Incentives are reduced to control Bitcoin’s supply.
Despite these challenges, the blockchain network is designed to adapt, ensuring stable transaction processing and network security.
Blockchain vs. Bitcoin
To clarify, blockchain is the underlying technology—a decentralized ledger system—while Bitcoin is one of the many cryptocurrencies utilizing this technology. Blockchain serves as the foundation for securely validating and recording transactions.
Scalability Issues in Blockchain
As the blockchain grows, scalability becomes a significant concern. Factors contributing to this include:
- Data Storage: Every node maintains a complete copy of the blockchain, requiring vast storage space.
- Computational Power: Solving increasingly complex problems demands significant resources.
- Energy Consumption: Mining consumes a substantial amount of electricity.
These challenges highlight the need for innovative solutions to support the continued growth of blockchain networks.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology offers a powerful framework for enhancing business operations. By adopting blockchain, companies can ensure greater security, transparency, and efficiency in their processes.
In upcoming articles, we’ll explore solutions to scalability issues, blockchain applications, and startup opportunities.
Blockchain technology offers a powerful opportunity to enhance and simplify your business operations. Embracing this technology now is crucial to staying ahead of the curve. With blockchain development as a service, you can benefit from high levels of security while seeing real-world applications expand rapidly.
Are you planning to develop MLM software?
Contact Us Today to explore the Advance features for you MLM Business!
